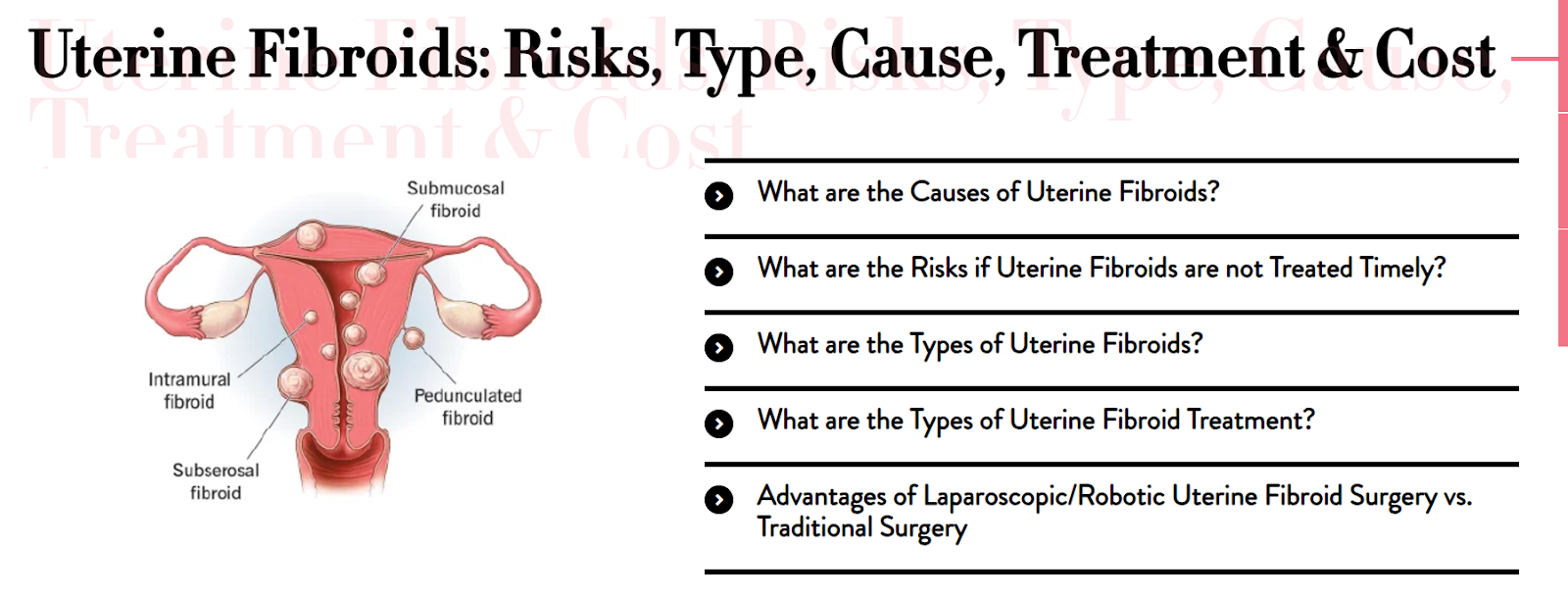
Uterine fibroids, also called leiomyomas, are non-cancerous tumours in the uterus. Uterine fibroids can develop in the uterine walls, on its outer surface or inside the main cavity of the uterus. They can range in size from smaller than a seed to as large as 10 cm in diameter or more, about the size of a mango and may develop as a single nodule or in clusters.
Uterine Fibroid Symptoms
Women with smaller fibroids are often asymptomatic and may not need treatment. However, women with larger uterine fibroids may experience the following symptoms:
Abnormal vaginal bleeding between periods
Heavy bleeding during periods
Post-menopausal bleeding
Lower abdominal pain
Pelvic pressure
Increased menstrual cramps
Increased frequency of urination
Pain during sexual intercourse
Chronic vaginal discharge
Constipation
Uterine Fibroid Causes
The exact cause of uterine fibroids remains unknown. However, certain genetic factors such as family history, prolonged exposure to estrogen and progesterone can influence the development of uterine fibroids.
Uterine Fibroids Diagnosis
Uterine fibroids are often identified during a routine pelvic exam. To confirm the diagnosis, a doctor may recommend the following tests:
Ultrasonography: This non-invasive imaging test uses soundwaves to take pictures of the uterus and detect the location of fibroids.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI detects the size and location of fibroids to identify their type. The test shows detailed images of fibroids that help a doctor assess the best treatment for the condition.
Computed tomography (CT) scan: This imaging scan creates detailed X-ray images of the fibroids from multiple angles.
Hysterosonography (HSG): In this test, a doctor uses a saline solution to expand the uterine cavity, making it simpler to get images of the fibroids.
Hysteroscopy: During this test, a doctor uses a small device with a camera through the vagina to examine the uterus.
Laparoscopy: In this procedure, the doctor makes an incision in the lower abdomen to insert a thin, camera-equipped tube for a detailed examination of the fibroids.
Uterine Fibroids Treatment
There is no single treatment for uterine fibroids; various approaches are available depending on the symptoms. If the size of uterine fibroids is small and an individual is asymptomatic, regular follow-ups with a doctor are important. However, if the fibroids are large, a doctor may recommend the following treatments:
Medicines used for the treatment of uterine fibroids work by targeting hormones that control the menstrual cycle. The doctor prescribes medicines such as GnRH (gonadotropin - releasing hormone) agonists, GnRH antagonists, progestin-releasing IUD (intrauterine device), and tranexamic acid (non-hormonal medicine).
One of the only permanent solutions for uterine fibroids, hysterectomy helps remove the uterus. It is important to remember that hysterectomy ends the ability to have children.
An abdominal myomectomy removes fibroids through a large cut in the stomach area. A doctor may suggest a myomectomy for cases involving multiple, large, or deeply embedded fibroids.
This procedure uses heat generated by radiofrequency energy to destroy uterine fibroids, alter their consistency, and shrink the blood vessels supplying them.
Uterine Fibroid Embolization
During this procedure, a surgeon inserts a thin tube in blood vessels that supply blood to the uterine fibroids. Then, the surgeon inserts tiny gel or plastic particles to block supply to the fibroids, causing them to shrink.
Uterine Fibroids Risk Factors
The factors that may increase the risk of uterine fibroids include:
Uterine Fibroids Complications
Uterine fibroids are generally benign and rarely interfere with pregnancy. They also often grow at a slow rate and tend to shrink when levels of reproductive hormones drop after menopause. However, in some cases, they can cause complications like heavy blood loss. Rarely, uterine fibroids can cause discomfort and complications at the time of pregnancy such as:
Fetal growth restriction
Preterm delivery
Placental abruption.
FAQs
What is the main cause of uterine fibroids?
It is not known what causes uterine fibroids. However, fibroids are usually non-malignant and extremely common amongst women. Prolonged exposure to estrogen and certain genetic factors can increase the risk of fibroids.
Can a woman live with fibroids?
Fibroids are common and many people may experience mild or no symptoms at all. For a person experiencing severe symptoms, uterine fibroids can significantly affect the quality of life. It is always best to speak to a doctor about the symptoms to help determine the best treatment plan.
Do uterine fibroids cause pain?
A majority of women are affected by uterine fibroids at some stage in their lives. Even though fibroids usually don’t cause any symptoms, when they do, pelvic pain is one of the most prevalent symptoms.
What is the best medicine for uterine fibroids?
The most effective medicine for uterine fibroids treatment is GnRHa (gonadotropin releasing hormone) agonists, including Zoladex, Synarel, and Lupron.
Comprehensive
Treatments for a Wide Range of Obstetrics & Gynaecology Conditions
Vaginal
Cyst Treatment
Ovarian
Cyst Treatment